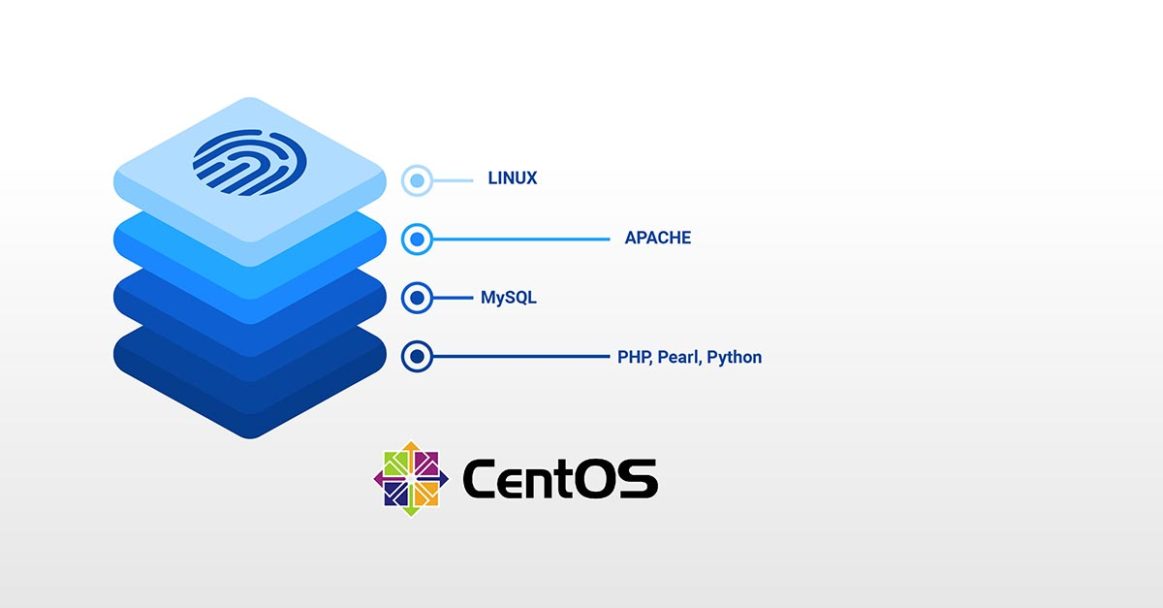
LAMP is an acronym of a very popular web stack – Linux, Apache, MySQL, PHP. All of the four components of LAMP are open-sourced and are suitable to deploy dynamic websites and web applications. In this tutorial, we will walk you through setting up a cloud server with the LAMP stack.
LAMP Stack: L – Linux
L in LAMP stands for Linux Operating System. With CloudSigma’s easy-to-use interface, you can deploy it within minutes.
Creating the machine
First, you have to create a machine. You can do that easily under CloudSigma’s Compute Section. For the purposes of this tutorial, you can use the following resources:
CPU: 8 GHz
RAM: 8 GB
SSD: 50 GB
You can mount the disk with CentOS 7.8 Server – 64bit Pre-Installed English with SSH, Python, Pip, Cloud-init, OpenSSL, and VirtIO support. After starting the machine, you can update all the existing repos and packages on the machine by running the following commands:
|
1 |
sudo yum update |
LAMP Stack: A – Apache
Apache (Apache HTTP Server) is an open-source web server software that can be used to serve the content on the web. More than 40% of the websites on the WWW – World Wide Web use it. To install the Apache HTTP Server, you can run the following command:
|
1 |
sudo yum install httpd |
Once the webserver is installed, you can use the following command to start it:
|
1 |
sudo systemctl start httpd.service |
Once it’s installed, you can go to the IP address on your web browser and you will see an output similar to this:
If you don’t see the above screen, it’s possible that your firewall is blocking the HTTP traffic. You can use the following commands and try again:
|
1 2 3 |
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service=http sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service=https sudo firewall-cmd --reload |
If you do not know the IP address, you can check it under CloudSigma account’s Compute Section:
You can also enable Apache to start on boot with the following command:
|
1 |
sudo systemctl enable httpd.service |
LAMP Stack: M – MySQL (MariaDB)
You can go ahead and install MySQL now that Linux and Apache are installed. With this tutorial, you can also install MariaDB, a MySQL replacement. MariaDB is a community-developed version of the MySQL project. You will store your website data in it:
|
1 |
sudo yum install mariadb-server mariadb |
Once the installation is complete, you can start MariaDB with the following command:
|
1 |
sudo systemctl start mariadb |
To increase the security, run the below script, and choose your preferences:
|
1 |
sudo /usr/bin/mysql_secure_installation |
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 |
Output: Enter current password for root (enter for none): OK, successfully used password, moving on... Setting the root password ensures that nobody can log into the MariaDB root user without the proper authorization. New password: password Re-enter new password: password Password updated successfully! Reloading privilege tables.. ... Success! For the rest, you can just click enter |
Again, you can choose to enable MariaDB to start on boot with the following command:
|
1 |
sudo systemctl enable mariadb.service |
LAMP Stack: P – PHP
PHP is a popular open-source scripting language generally used for building dynamic web pages. You can install it using the command:
|
1 |
sudo yum install php php-mysql |
After this, you need to restart the Apache webserver for it to work seamlessly with PHP:
|
1 |
sudo systemctl restart httpd.service |
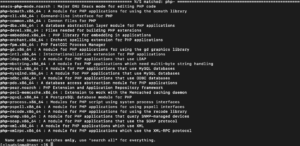
PHP has a vast library of modules that you can use in your application. Find the available libraries using the given command and it will provide you with a list:
|
1 |
sudo yum search php- |
Install the above modules using the yum command:
|
1 |
sudo yum install <<ModuleName>> |
You can create a sample PHP file to test it out. Create a file – /var/www/html/test.php and add the following contents to it:
|
1 2 3 |
<?php phpinfo(); ?> |
Now, when you go to the URL – https://IPaddress/test.php, you will see the following content:
Finally, you have successfully set up your LAMP Stack!
Happy Computing!
- Removing Spaces in Python - March 24, 2023
- Is Kubernetes Right for Me? Choosing the Best Deployment Platform for your Business - March 10, 2023
- Cloud Provider of tomorrow - March 6, 2023
- SOLID: The First 5 Principles of Object-Oriented Design? - March 3, 2023
- Setting Up CSS and HTML for Your Website: A Tutorial - October 28, 2022