Python is a high-level, general-purpose programming language with emphasis on code readability. It supports various programming paradigms, for example, structured, object-oriented, and functional programming. Oftentimes, Python is described as “batteries included”, thanks to its comprehensive standard library.
In this guide, we are going to learn various ways of removing whitespaces from a string in Python.
Prerequisites
To perform the steps demonstrated in this guide, you will need the following components:
-
- A properly-configured Linux machine, for example, a Ubuntu VPS on CloudSigma.
-
- A properly-configured Python development environment. Check out configuring a Python development environment on Ubuntu.
-
- A suitable text editor, for example, Brackets, VS Code, Sublime Text, Vim/NeoVim etc.
Step 1 – Creating a Python Script
For demonstration purposes, we are going to create a Python script remove-space.py and put all our codes there. Then, we are going to run the script with the help of the Python interpreter.
First, create the Python script:
|
1 |
touch remove-space.py |
Open the script in a text editor:
|
1 |
nano remove-space.py |
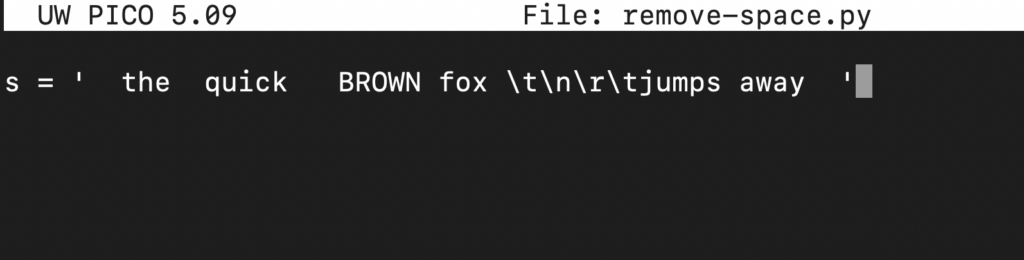
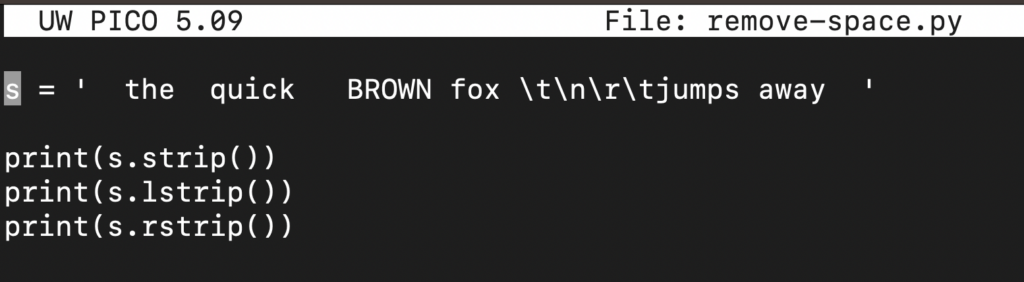
Next, we are going to create a string variable s and assign a string:
|
1 |
s = ' the quick BROWN fox \t\n\r\tjumps away ' |
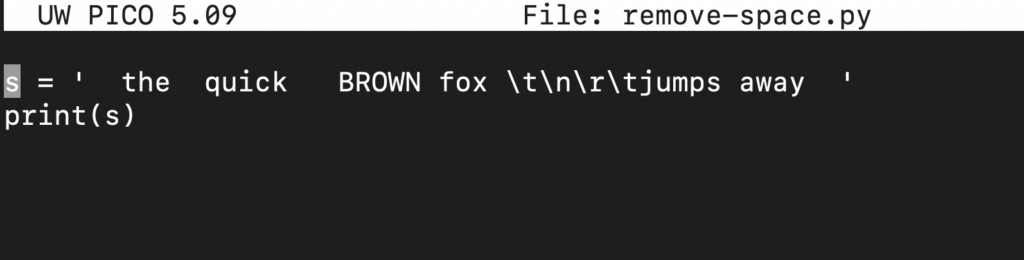
If we include the print() function, we can see how the string is interpreted:
|
1 2 |
s = ' the quick BROWN fox \t\n\r\tjumps away ' print(s) |
Here,
-
- The
print()function is taking a string as an argument.
- The
-
- The
print()function can interpret backslash characters.
- The
Run the script:
|
1 |
python remove-space.py |

Step 2 – Removal of Lead/Tail Spaces
With the help of the strip() function, we can remove the leading and tailing characters of a string.
The following code demonstrates using the strip() function on the variable s:
|
1 2 |
s = ' the quick BROWN fox \t\n\r\tjumps away ' print(s.strip()) |
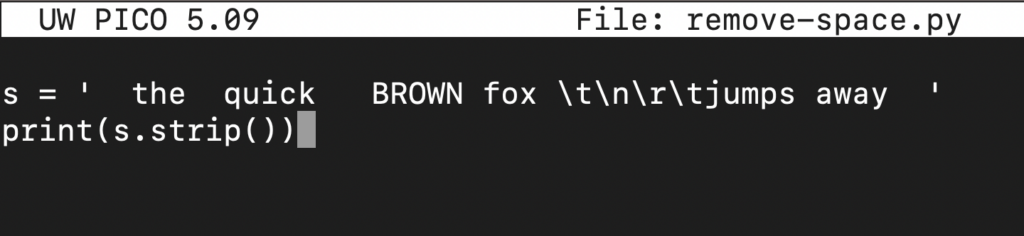
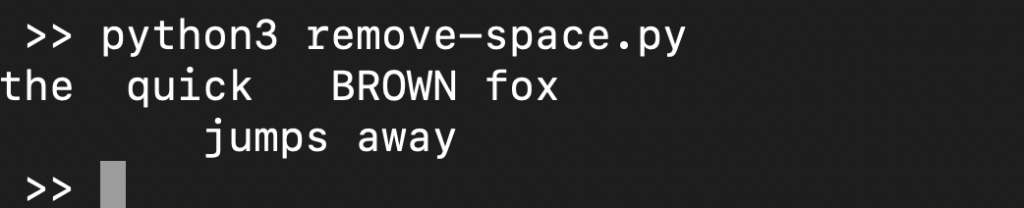
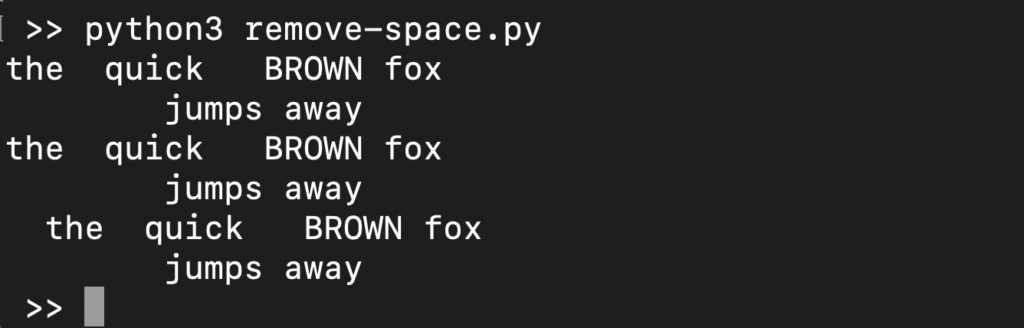
Note that the strip() function removes all the leading and tailing spaces. If you want to remove just the leading or tailing spaces, then use lstrip() or rstrip() respectively:
|
1 2 3 4 5 |
s = ' the quick BROWN fox \t\n\r\tjumps away ' print(s.strip()) print(s.lstrip()) print(s.rstrip()) |
Step 3 – Removal of All Whitespaces
With the help of the replace() function, we can replace contents in a string. Taking advantage of this feature, we can replace all the whitespaces with nothing, thus removing them.
Let’s put the replace() function in action. Check out the following code:
|
1 2 3 |
s = ' the quick BROWN fox \t\n\r\tjumps away ' print(s.replace(" ", "")) |
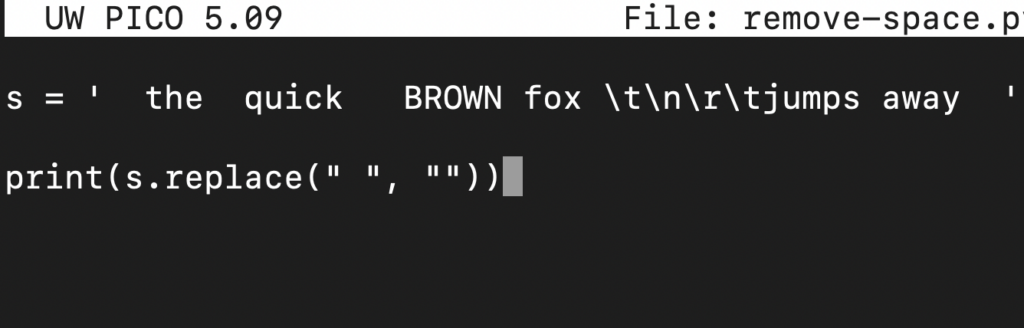
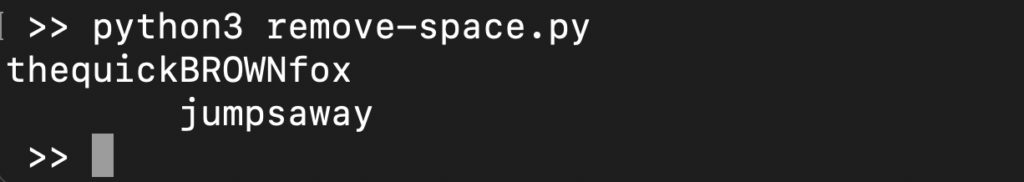
Here,
-
- The first parameter of
replace()describes what pattern to look for in the given string.
- The first parameter of
-
- The second parameter of
replace()describes what will be the replacement content.
- The second parameter of
Step 4 – Removal of Whitespaces using split() and join()
In this section, we are going to use the split() and join() functions.
-
split(): It takes a string and breaks it up into a list. The breaking points are determined by a delimiter.
-
join(): It takes the list and puts it back into a single string. The parts are joined using a single whitespace (” “).
Let’s put these functions in action. Have a look at the following code:
|
1 2 3 |
s = ' the quick BROWN fox \t\n\r\tjumps away ' print(" ".join(s.split())) |
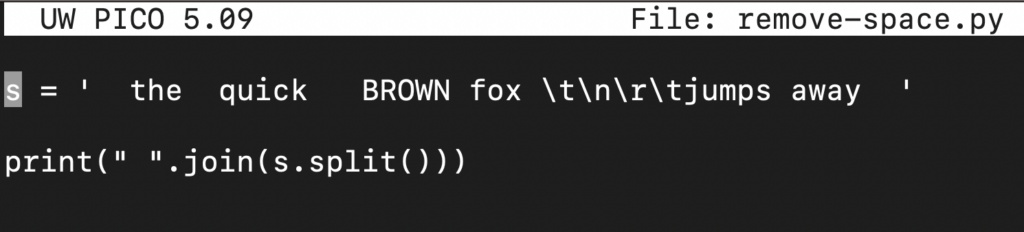
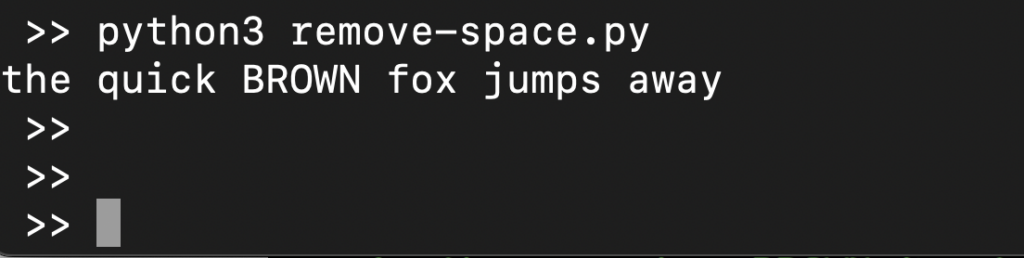
Here,
-
- We have combined the usage of
split(),join(), andprint()in a single line.
- We have combined the usage of
-
- The output of the
split()function is passed as an argument for thejoin()function.
- The output of the
-
- The output of the
join()function is passed as an argument for theprint()function.
- The output of the
Step 5 – Removal of Whitespaces using translate()
In Python, the translate() function replaces specified characters with characters defined in a dictionary or a mapping table.
In this example, we are going to use the string.whitespace dictionary that contains all the whitespace characters.
Have a look at the following code:
|
1 2 3 4 5 |
import string s = ' the quick BROWN fox \t\n\r\tjumps away ' print(s.translate({ord(c): None for c in string.whitespace})) |
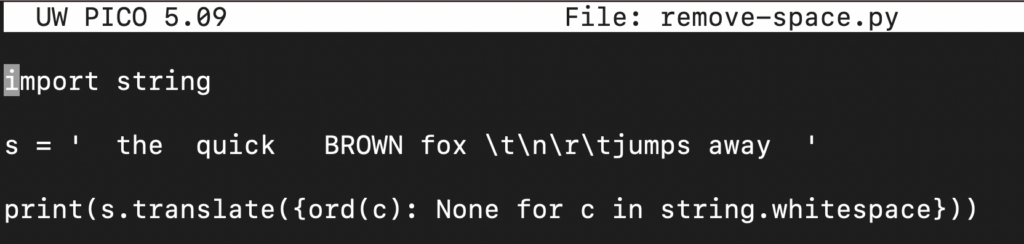

Step 6 – Removal of Whitespace using Regex
Regular expression (or “regex” for short) is a powerful feature in many programming languages. Any regular expression will consist of a series of characters that construct a search pattern. A regular expression can be used to check if a string contains the specified pattern.
Python also supports regex, significantly improving its text manipulation capabilities. In this section, we will use regex to eliminate any whitespace character found on our test string.
Take a look at the following code:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 |
import re s = ' the quick BROWN fox \t\n\r\tjumps away ' print('Remove all spaces:\n', re.sub(r"\s+", "", s), sep='') # \s matches all white spaces print('Remove leading spaces:\n', re.sub(r"^\s+", "", s), sep='') # ^ matches start print('Remove trailing spaces:\n', re.sub(r"\s+$", "", s), sep='') # $ matches end print('Remove leading and trailing spaces:\n', re.sub(r"^\s+|\s+$", "", s), sep='') # | for OR condition |
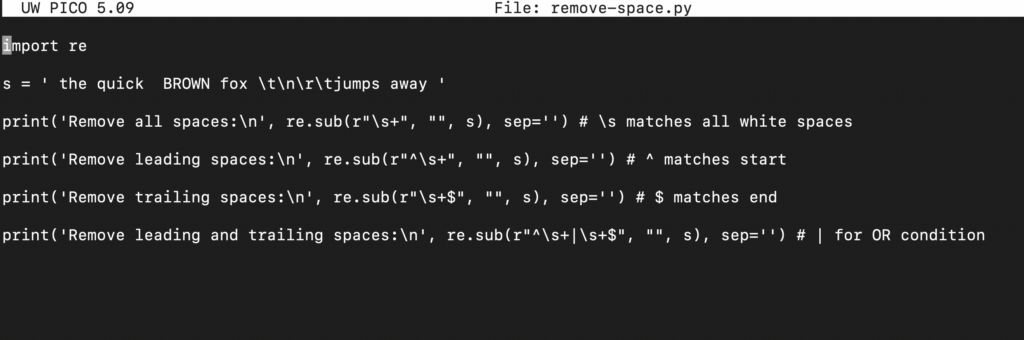
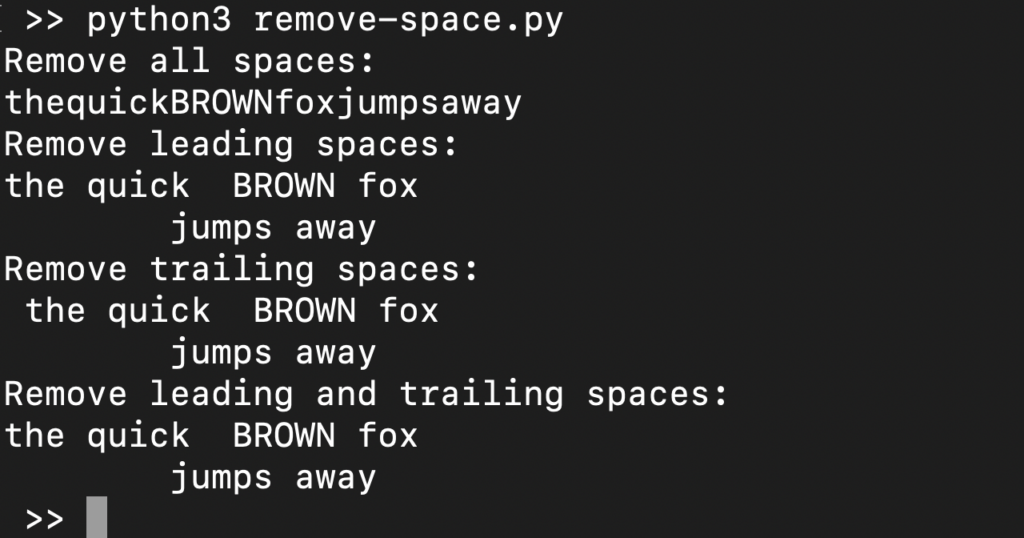
Here,
-
- We are importing
re, a dedicated package for working with regular expressions.
- We are importing
Final Thoughts
In this guide, we demonstrated various ways of dealing with whitespaces in a string with Python. In the process, we also learned simple usage of various functions like split(), join(), replace(), translate(), etc.
Interested in learning more about Python? Check out the following guides:
- Removing Spaces in Python - March 24, 2023
- Is Kubernetes Right for Me? Choosing the Best Deployment Platform for your Business - March 10, 2023
- Cloud Provider of tomorrow - March 6, 2023
- SOLID: The First 5 Principles of Object-Oriented Design? - March 3, 2023
- Setting Up CSS and HTML for Your Website: A Tutorial - October 28, 2022



