Java Runtime Environment (JRE) is a critical aspect of the Java programming language, enabling the execution of Java applications and programs on various platforms. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into what the Java environment entails, the functions of JRE, and its differences from other Java components.
What is the Java Runtime Environment?
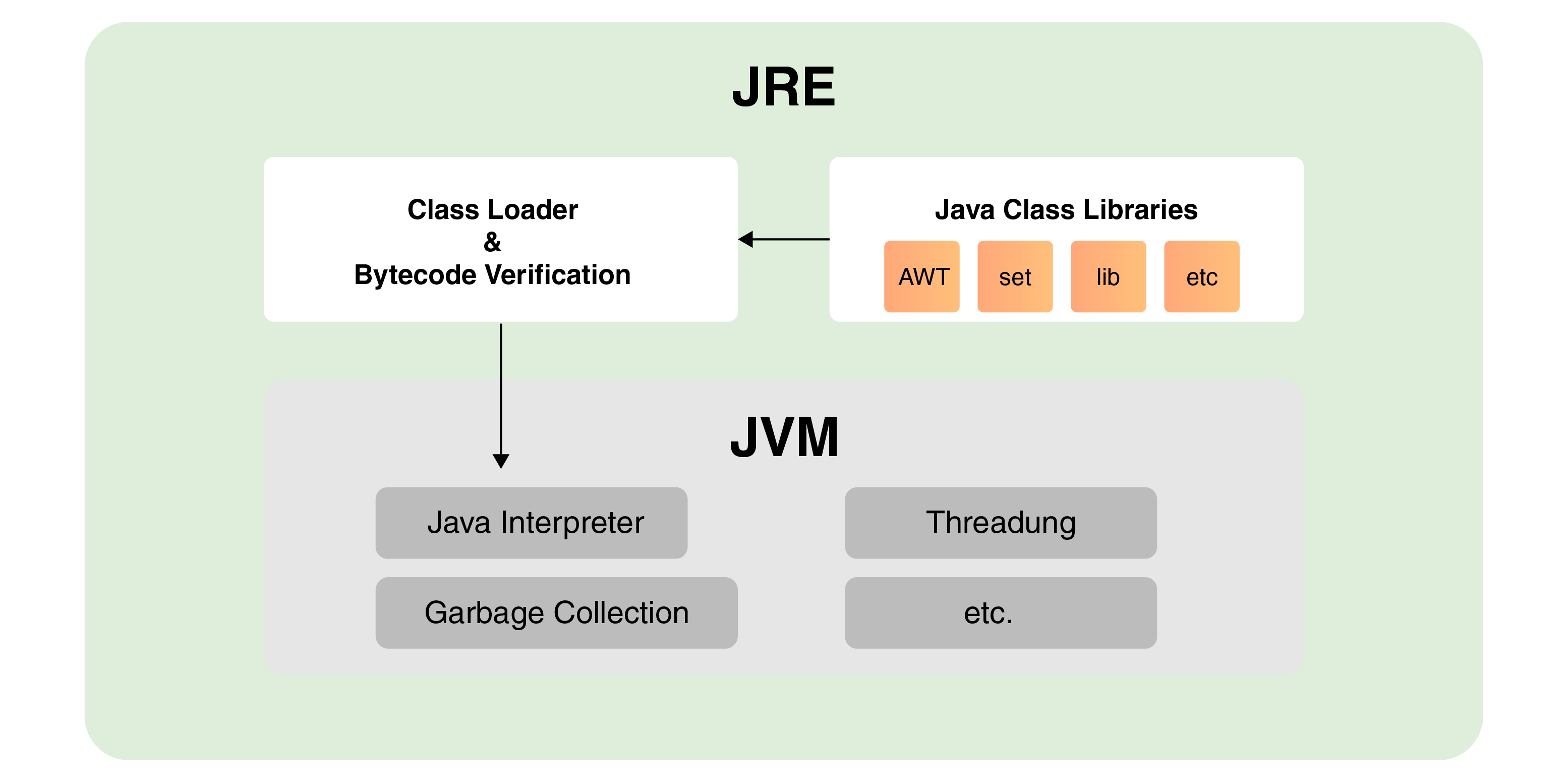
The Components of JRE
Java Virtual Machine (JVM)
Class Libraries
Java Application Launcher
Java Plug-in
What is JRE’s Role in Java Development
Differences Between Java Runtime Environment (JRE) and Java Development Kit (JDK)
JRE is primarily responsible for executing Java applications and applets. It provides the necessary runtime environment, including JVM and class libraries, but it does not include development tools such as compilers and debuggers.
In essence, JRE is for running Java programs, while JDK is for developing and running them.
Why is Understanding the Java Environment Important?
Having a solid understanding of the Java Runtime Environment is crucial for developers and individuals interested in Java programming.
Here’s why:
✓ Troubleshooting: Knowledge of the Java environment aids in identifying and resolving runtime errors and compatibility problems.
✓ Optimization: Developers can optimize Java applications by understanding how JRE interacts with the underlying system.
✓ Security: Awareness of JRE helps in implementing security measures and safeguarding Java programs from potential threats.

Differences Between Java Runtime Environment (JRE) and Java Development Kit (JDK)
Java Runtime Environment (JRE) is a set of software tools that provides the runtime environment necessary for executing Java applications. It includes a virtual machine (JVM) and class libraries, enabling Java programs to run on different operating systems.
The JRE is crucial because it bridges the gap between Java applications and the underlying operating system. It allows Java programs to be executed on various platforms, following the “write once, run anywhere” principle.
The JRE works by taking Java bytecode, which is generated from human-readable Java code, and translating it into machine code, making it executable on the host system.
The components of the JRE include the Java Virtual Machine (JVM), class libraries, Java application launcher, and Java plug-in. In conclusion, the Java Runtime Environment (JRE) plays a vital role in the Java language by enabling the execution of Java applications on different platforms.
Its components, including the Java Virtual Machine and class libraries, contribute to the “write once, run anywhere” principle, making Java a versatile and widely-used programming language. Understanding the Java environment is essential for developers to create efficient, compatible, and secure Java applications.
Remember, Java Runtime Environment is distinct from the Java Development Kit (JDK), which offers additional development tools for programmers. Embracing the capabilities of JRE empowers developers to create powerful Java applications that can run seamlessly across various operating systems.
Keep exploring the Java universe, and unlock new possibilities with the Java Runtime Environment!


